
What is a Stroke?

A stroke is a medical emergency that could cause major disability and even death. Strokes are common and a leading cause of death in the United States: each year, more than 795,000 people in the nation have a stroke; of these, 137,000 die. In fact, every 40 minutes, someone has a stroke in the US; every 3.5 minutes, an American dies from a stroke. Nearly one in four people who have a stroke have had one in the past.
Because of the effects they have on the body, strokes are a major cause of long-term disability. The condition reduces mobility, or ability to get around, in more than half of the survivors aged 65 and older.
Strokes are also expensive – stroke-related costs in the US were almost $53 billion between 2017 and 2018. The costs cover healthcare services, medicine, and missed days of work.
But what exactly is a stroke? Here is what you need to know.
Blood vessels carry oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to the brain and the rest of the body. Cells of the body use the oxygen and nutrients to function. A stroke happens when something prevents the blood from reaching certain parts of the brain, thereby starving the affected brain cells of the oxygen and nutrients they need. Without oxygen, brain cells can begin to die within minutes.
Symptoms of Stroke
Symptoms of a stroke can vary, depending on the part of the brain affected by lack of blood flow.
Symptoms of a stroke come on suddenly with a rapid onset and may include:
- Numbness, tingling or weakness in the person’s face or in their arm or leg, especially on one side of the patient’s body
- Confusion
- Trouble seeing – may be in one or both of the patient’s eyes
- Difficulty talking or understanding speech
- Dizziness, loss of balance, loss of coordination, or difficulty walking
- Headache that is severe and with no known cause
If you or someone else experiences these symptoms, seek help immediately.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Stroke
Doctors perform a physical exam and a number of tests to diagnose a stroke. The physical exam includes listening to the patient’s heart and checking their blood pressure. The doctor will perform a neurological exam to assess the patient’s mental status and check the patient’s ability to feel pain or a light touch. They will also evaluate motor function and balance by having the patient pull and push against the doctor’s hand and watching the patient stand and walk.
Blood tests cannot determine if a patient has had a stroke, but they can help determine how quickly the patient’s blood clots. Blood glucose tests can measure the amount of sugar in the blood, as blood glucose levels are often higher during an acute stroke.
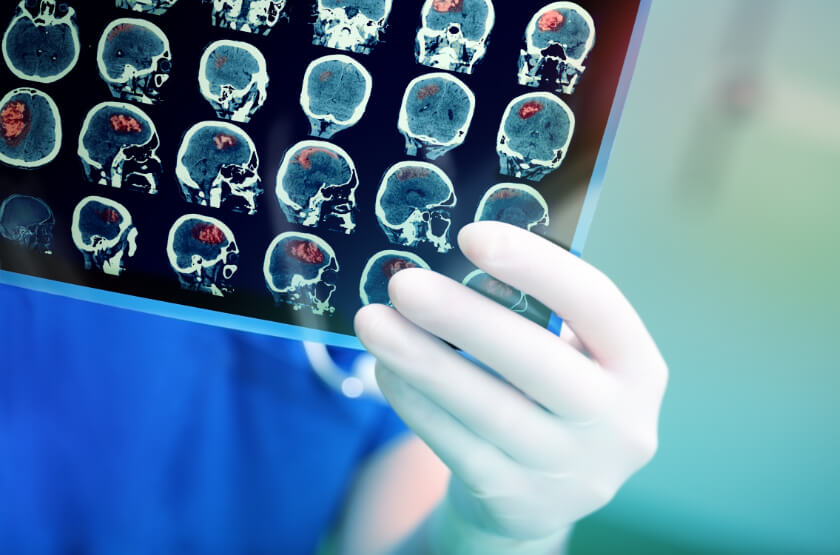
Doctors rely on imaging to diagnose a stroke. A CT scan, which compiles a series of x-rays to create a 3D image, can show bleeding in the brain, signs of an ischemic stroke, tumors, or other conditions that resemble strokes. Images created by an MRI can show damage to brain tissue caused by an ischemic stroke and brain hemorrhages. A carotid ultrasound creates detailed images of the carotid arteries in the neck, along with any plaques that may be there.
For more information on strokes, their causes, diagnosis, and treatment, consult with a doctor or radiologist. The more you know about strokes, the faster you can respond.